Based on a new built-in Bullet Physics Engine in Shade3D ver.16, Physics Assistant provides a simple way to calculate physics simulation.
Physics Assistant (Free)
*Compatible with Shade3D ver.16 Standard and Professional version (Both Download and Subscription version)
Installing the Physics Plugin and Physics Assistant in Shade3D
On Windows:
1. Unzip the file Physics_Assistant.zip. Nested inside the top folder you will find a folder named plugin, for installing the physics plugin itself, and a folder named widget, which is for installing the Physics Assistant widget UI.
2. In Explorer, navigate to Users > (name of your user folder) > Documents > Shade3D > Shade3D ver. 16. Both the plugin and widget should be installed to subfolders (plugins and widgets, respectively) in this location.
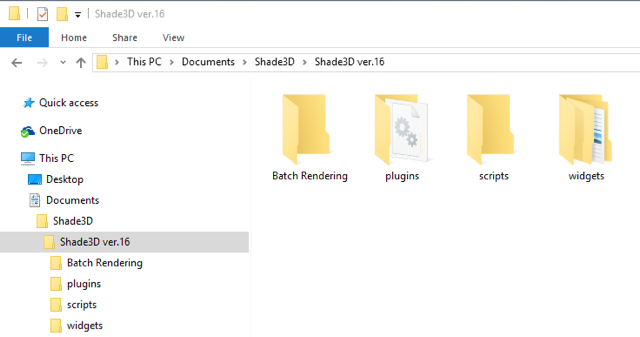
3. The file to move to the plugins folder is:
Physics_Assistant > plugin > win >PhysicsCore64.dll
4. The folder to move to the widgets folder is:
Physics_Assistant > widget > shade_physics_assistant
(Be sure to move the entire folder, not just the folder's contents.)
Installation is complete. Start (or restart) Shade3D, and check that Physics Assistant is listed in the Scripts menu.
On Mac:
1. Unzip the file Physics_Assistant.zip by right-clicking (or Control-clicking) and selecting Open. Nested inside the top folder you will find a folder named plugin, for installing the physics plugin itself, and a folder named widget, which is for installing the Physics Assistant widget UI.
2. In Finder, navigate to Users > (name of your user folder) > Shade3D > Shade3D ver. 16. Both the plugin and widget should be installed to subfolders (plugins and widgets, respectively) in this location.
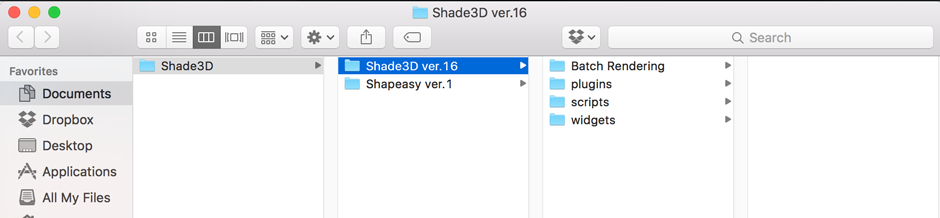
3. The file to move to the plugins folder is:
Physics_Assistant > plugin > mac > PhysicsCore.shdplugin
4. The file to move to the widgets folder is:
Physics_Assistant > widget > shade_physics_assistant
(Be sure to move the entire folder, not just the folder's contents.)
Installation is complete. Start (or restart) Shade3D, and check that Physics Assistant is listed in the Scripts menu.
Using Physics Assistant
1. After installing both the Physics plugin and Physics Assistant widget, start Shade3D and open the scene you wish to use with the Physics plugin.
2. Select Scripts > Physics Assistant. The Physics Assistant window opens.
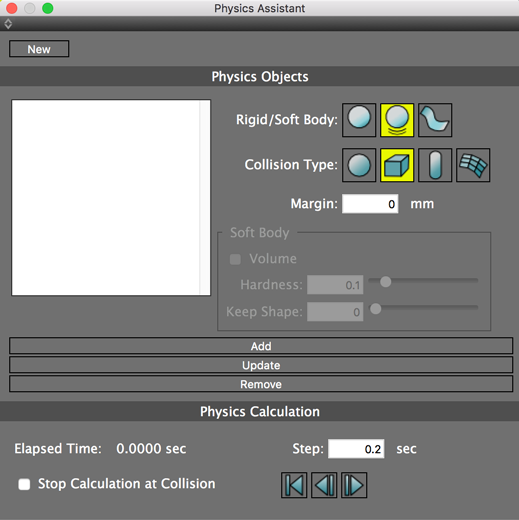
3. For each object you wish to include in the physics calculation, decide whether it should be a static rigid body (an object that should not move, such as the ground or a wall), a dynamic rigid body (an object such as a billiard ball that can collide with other objects), or a soft body (an object such as a cushion or cloth).
In the following example we have a ball and a box that will fall down a ramp, colliding with objects at the bottom. We don't want the ramp to move, so that should be a static rigid body. Each ball and box should be a dynamic rigid body.
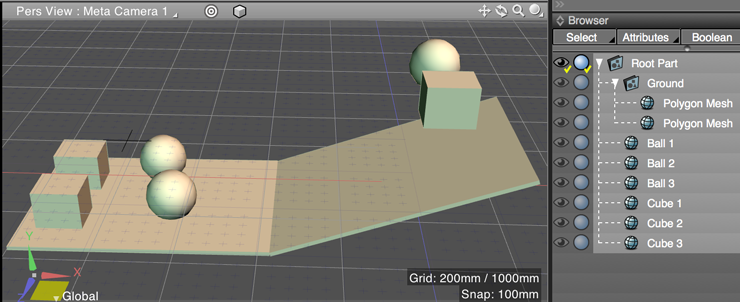
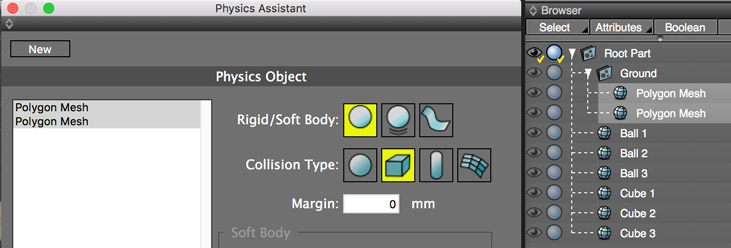
In the Browser, select the first object (the order is irrelevant) and choose the appropriate button in the top row of the Physics Assistant.
4. Next, for the Collision Type, select which shape the object most closely resembles: a ball, a box, a capsule, or (for more complex shapes) a mesh. Mesh collisions take the longest to calculate, so only use when necessary.
5. Click the Add button to add the object to the list of physics objects.
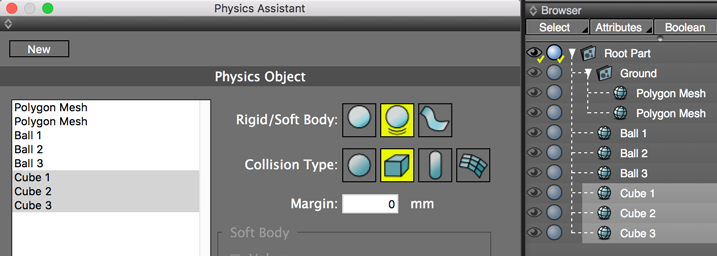
6. Repeat for the other objects you wish to add to the physics calculation. If you make a mistake, adjust the settings for the physics object and click the Update button. To remove a physics object from the calculation, select it and click Remove. If multiple objects are to be treated identically for the physics calculation, you can select those objects at one time and add them together.
7. Once you have finished adding objects to the list of physics objects, adjust the Step length (how much time to advance for each physics calculation) if you wish.
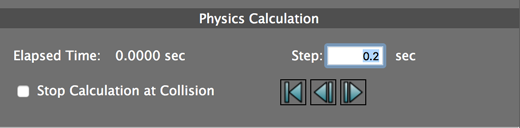
8. Click the Step Forward button to advance the specified length of time and calculate the position of each object at that instant. Depending on the complexity of the calculation, there may be a slight delay.
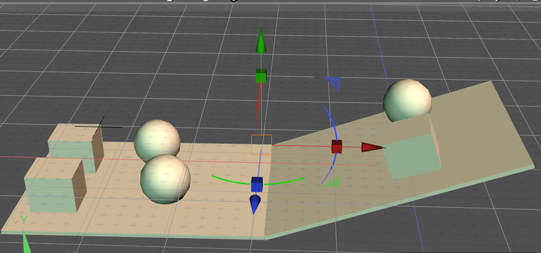
After stepping forward 0.6 seconds
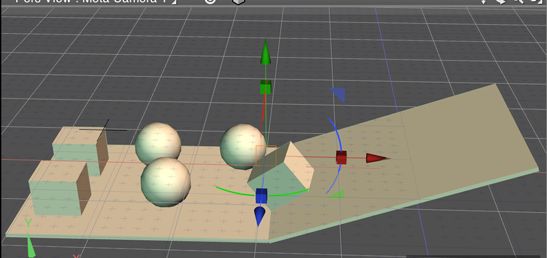
After stepping forward 1.6 seconds
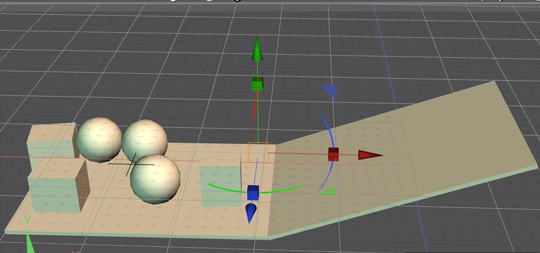
After stepping forward 2.8 seconds
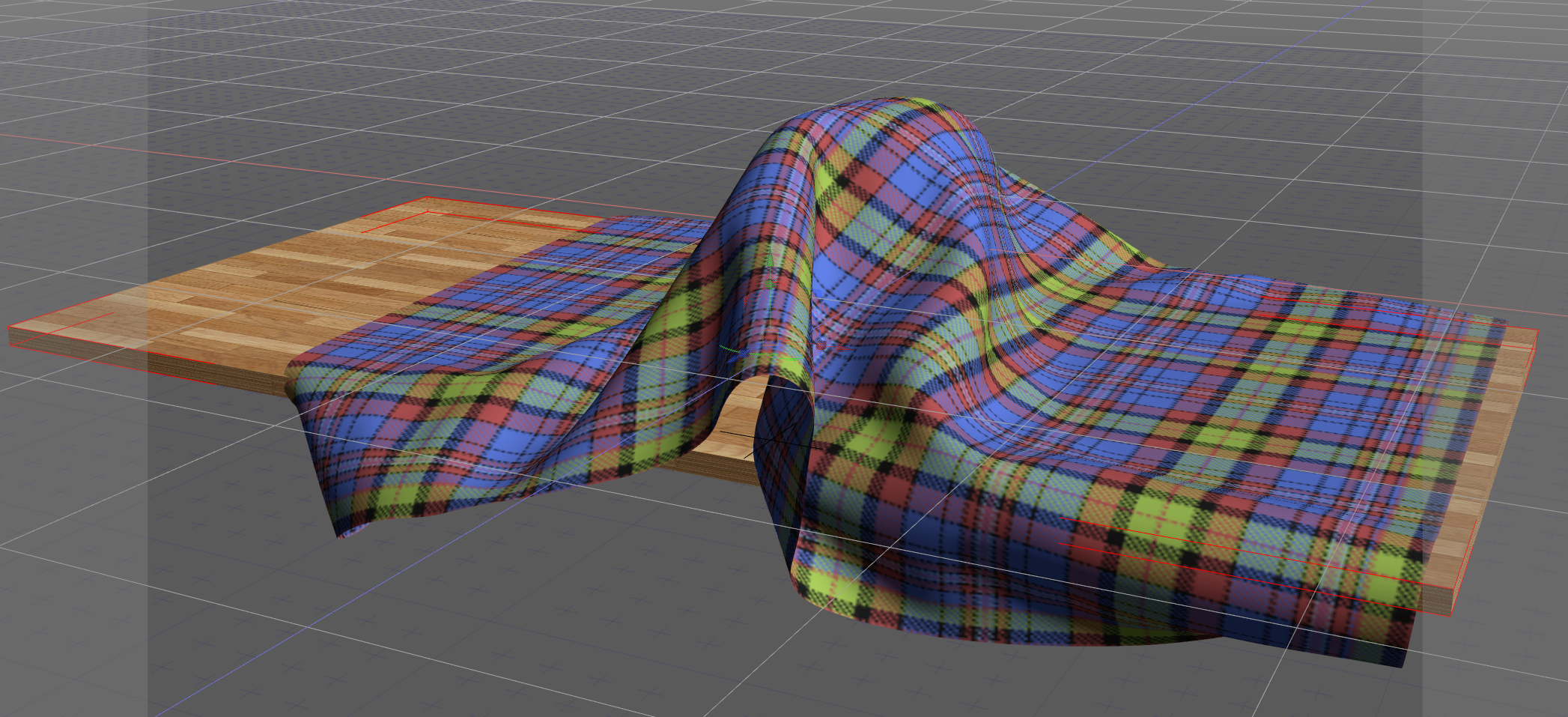
In our next example, a cloth-like soft body has been placed over a static, rigid ball. For the cloth, a margin of 50mm has been added. Advancing forward in the physics calculation shows the cloth falling over the ball and wrapping around it.
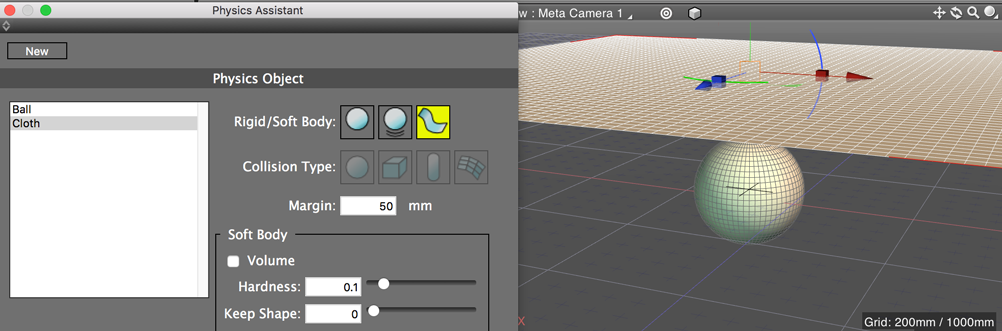
Before starting the physics calculation (0 sec elapsed). A margin of 50mm has been added to the cloth object.
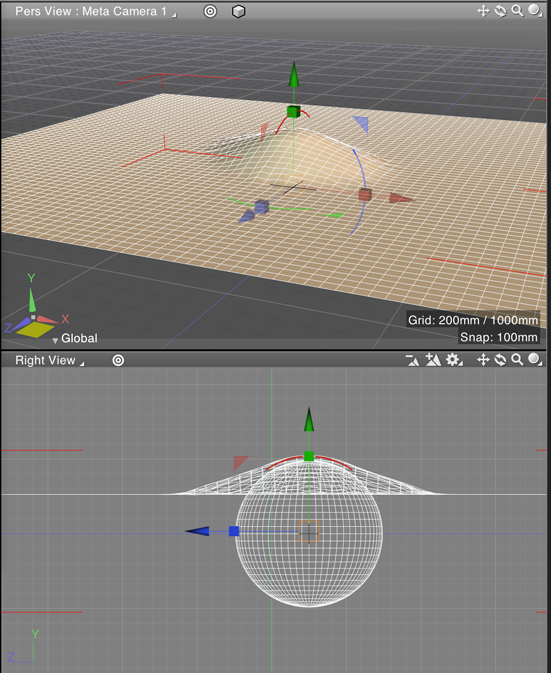
0.4 sec elapsed
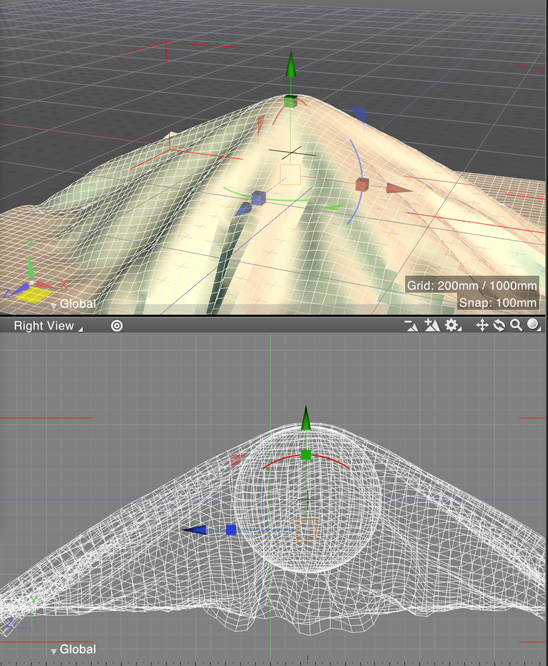
0.6 sec elapsed
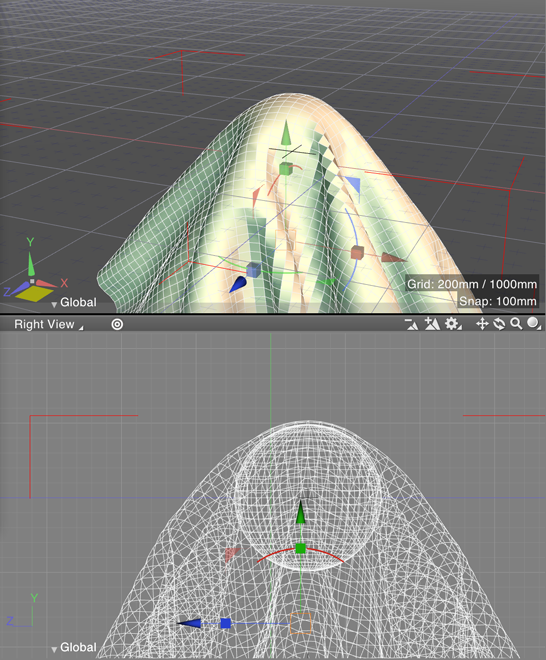
0.8 sec elapsed
Advanced Settings
If a soft body slips through other objects, add a margin (thickness) to it. Click the Update button after making changes.
For soft bodies with volume (anything thicker than a simple cloth), adjust the Hardness and Keep Shape settings until you get the desired effect.